Next Level Podcast with Host Tavis Piattoly, MS, RD, LD
Tavis Piattoly, MS, RD, LDN
Host and Presenter
Sports Dietitian
Co-founder of My Sports Dietitian
In this episode of the Next Level, Podcast we’ll focus on what is inflammation and how it impacts recovery, which foods are inflammatory, which foods are anti-inflammatory, and nutrition strategies to enhance the recovery process to minimize inflammation.
How Can I....?
- Reduce how sore I feel after my workouts, especially the next day?
- Have more energy during my training session tomorrow?
- Rebuild muscle tissue faster after an intense lifting session?
- Have the same amount of energy at the end of a long season as I did at the end?
All of these questions make up the complex topic of recovery. Recovery is such a broad term in that it can mean so many things. When someone asks me what I can do to recover faster, I usually respond with multiple questions to see what specifically he or she is looking to accomplish or what may be causing a specific problem.
Inflammation
Inflammation is a normal process that occurs when:
- We lift weights (inflamed muscle tissue, muscle damage)
- We sustain an injury (i.e. broken ankle, torn ACL, concussion)
Inflammation also occurs when we specific foods or drink specific beverages such as:
- Foods and fluids high in sugar
- White floured carbohydrates (enriched white flour (i.e. pancake mix), white bread
- Foods high in saturated and trans fatty acids (i.e. Red Meat, Omega 3 Oils, Baked Products like cookies, cakes, pies, etc)
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Fried Foods
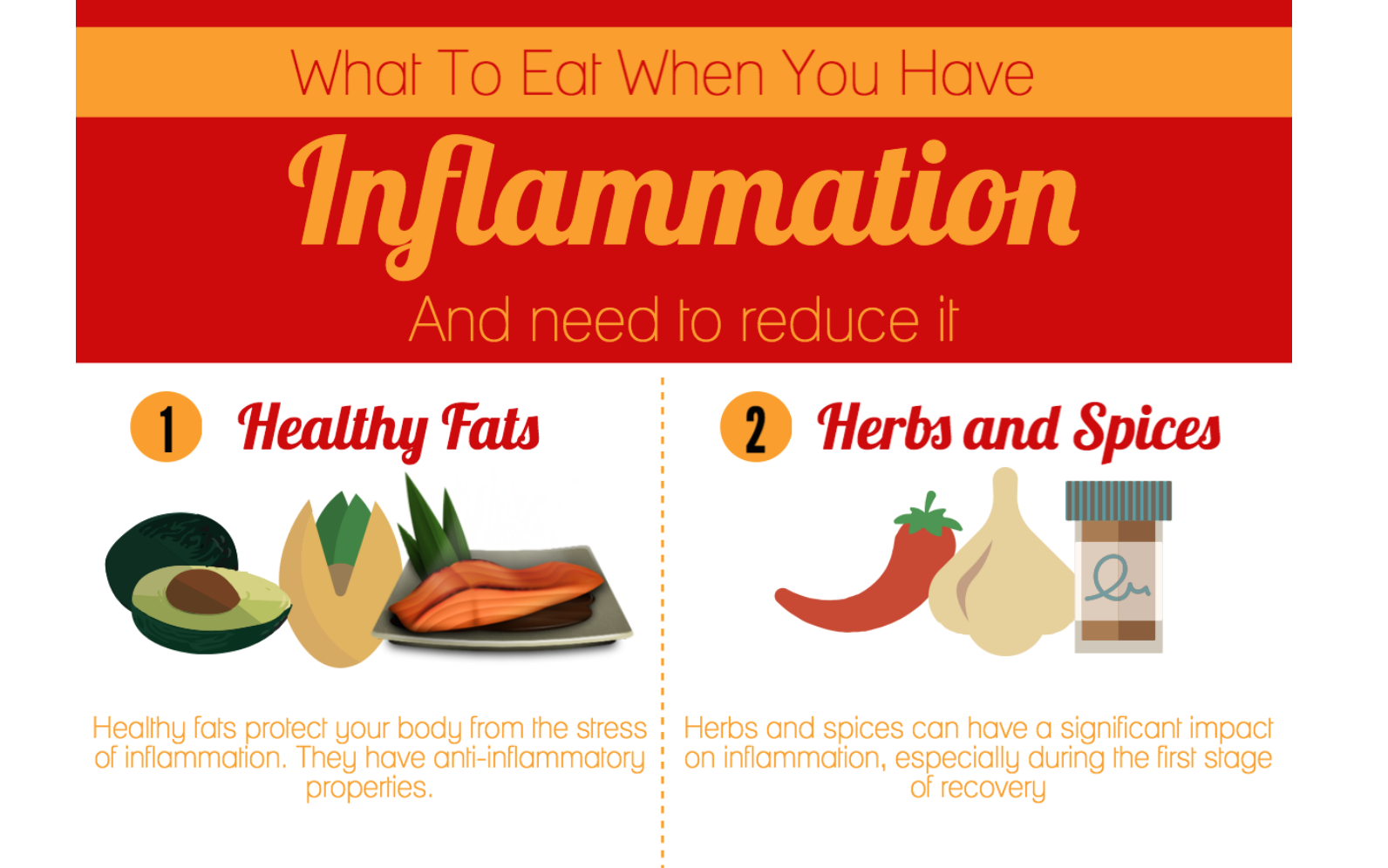
We can reduce the amount of inflammation by eating specific foods that are nutrient dense and contain antioxidants such as:
- Fresh fruit (Tart Cherries or Cherry Juice, Berries, Apples)
- Fresh Vegetables (Dark Green Veggies are best)
- Omega 3 Fats (i.e. Walnuts, Salmon, Mackeral, Halibut, Tuna, Fish Oil)
- Spices (Turmeric, Curry, Curcumin, Cinnamon, Basil, Cloves, Oregano, Thyme
Podcast Transcript
0:00 The Next Level Podcast Intro and Welcome by Tavis Piattoly
1:22 What is inflammation and what causes it?
- Inflammation is the body’s natural immune response and there are several things that cause it such as infections or injuries.
- Localized inflammation can occur when we sprain an ankle or have another injury. Inflammation can also occur systemically, which affects organs and internal structures.
- Long-term inflammation has been linked to dementia, heart disease, age-related diseases, chronic pain, and even some auto-immune diseases.
- Other things that can cause inflammation: lack of sleep, stress, pollution exposure, smoking, not getting enough exercise, and diet
4:13 What foods can contribute to inflammation in the body?
- Sugar and refined carbohydrates (white rice, bread, enriched grain products), particularly high fructose corn syrup. When we eat these foods it results in a rapid increase in our blood sugar which triggers an insulin response.
- The only time we want insulin to be high is post-workout to help with recovery
- Another food that can contribute to inflammation are omega-6 rich oils such as vegetable oils. Our body can get out of balance when we consume too many omega-3 fatty acids. It is best to limit these in the diet rather than completely eliminate them. Corn, safflower and soybean oil also contain higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Red meat produces a chemical that triggers an inflammatory response in the body. Try limiting red meat intake as much as possible. If choosing red meat, try to pick grass fed if possible because animals that have been grass-fed contain higher omega-3s and decreased omega-6s.
- Partially hydrogenated oils are trans fats and these should be avoided completely as they contribute to inflammation and can cause other negative health consequences.
10:57 What are the best foods to eat to reduce inflammation?
- Fruits and veggies. The majority of antioxidants, nutrients, and phytochemicals come from fruits such as blueberries, raspberries, blackberries, cherries. Particularly tart cherry juice and blueberries which contain heat shock proteins that can reduce the inflammatory response. The goal is to have a wide variety of fruits to maximize inflammation.
- Vegetables like dark leafy greens are rich in antioxidants and other nutrients. Try to spread out fruit and vegetable intake throughout the day. Another vegetable to incorporate is celery which has over 20 antioxidant compounds. And last but not least the cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower
- Herbs, which we add to foods. Cayenne pepper, turmeric, ginger, basil, thyme, ground cinnamon, and oregano are all anti-inflammatory herbs and spices that can be added throughout the cooking process
- Fatty fish and fish oil suppresses the release of cytokines which increase inflammation. Omega-3 rich foods include salmon, trout, herring, mackerel, anchovies, and sardines. If you don’t like fish you can opt for a fish oil supplement. There is a separate podcast on fish oil supplements. But the take home message is to not buy a generic fish oil supplement, you need a high-quality brand such as Nordic Naturals. Other foods high in omega-3s are walnuts, almonds,
- Whole grains (barley, oatmeal and brown rice), and olive oil can also reduce inflammation. Add olive oil to salads, vegetables, add 1-2 tbsps to any food to get some extra calories and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- At the end of the day we don’t want to eliminate inflammation entirely but we want to minimize it to aid the recovery process (ex. decrease muscle soreness)
20:40 Closing Remarks by Tavis Piattoly
Download Infographic








Facebook comments